Law
7 Things To Ask Your Lawyer Before Selling Your House During Divorce
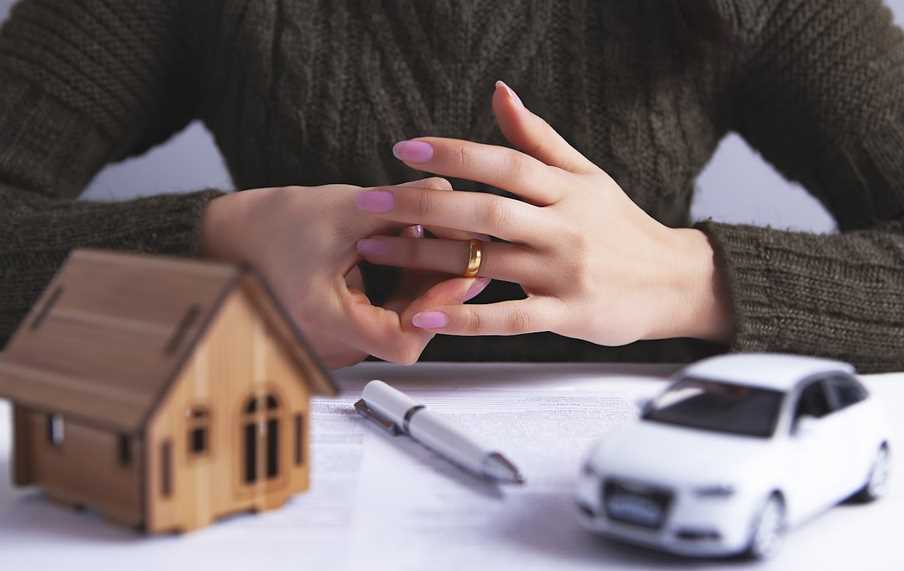

Most divorces end up including the sale of jointly owned properties from the union, and, sometimes, these properties include the family’s home. This can be a challenging process, unless handled with the right tact and legal strategy.
This post will reveal the top questions you’ll need to ask your lawyer before selling your house during divorce.
- How Will You Divide Personal Property?
Personal property refers to anything you own that isn’t real estate. How are you and your spouse going to share that? If you have a pre-nuptial agreement, then you might be guided by it during the sharing process. But, if not, you’ll need as much guidance as you can get if you can’t reach an immediate consensus between yourselves.
If certain things hold different levels of importance to any one of you, then the one to whom a ring isn’t as important might decide to let the other have it. But, sometimes, it’s not that easy. If you can’t reach an agreement, your lawyer might be able to help you by guiding you according to the laws that might aid you in your case or by negotiating on your behalf, which is a good thing, given a lawyer’s negotiations experience is more than that of the average person.
- Who Will Live In Our Home And For How Long?
You may also need to ask your lawyer to help you decide who gets to stay in the house and whether they can keep doing so while the house is on the market. If you and your spouse have any kids who are in school, then the spouse with primary custody to the kids could stay in the house for the benefit of the children. In this case, it might also be a good idea to put off the idea of selling your home until the end of your children’s school year, so their academics won‘t be drastically impacted.
There might be other factors that might help direct the answer to this question, so have your lawyer help you through your unique situation.
- While Waiting For A Buyer, Who Services The House’s Mortgage?
Someone has to pay for your house’s mortgage while it’s on the market if it’s to stay up to date with its mortgage servicing. If only one spouse was making money in the marriage, yet it’s the dependent spouse that has to stay in the house while it’s on the market, then they might not be able to pay for the mortgage.
Working this out with your lawyer in advance helps you stay ahead of potential problems.
- How Will I Select A Real Estate Agent?
If you and your spouse have already agreed on which realtor you’ll be using, then it’s a good idea to include it in your separation agreement, so it’s clear. If, however, you can’t agree, then your separation agreement will need to include the criteria you’ll use for choosing. Your attorney will help you draft this criterion.
While your realtor will be representing both your interests, if one spouse makes the decision on who the realtor will be, they’re most likely to be met with resistance than if, say, one spouse makes a list of three to five realtors and the other spouse chooses a house buying company in Dutchess County NY, or wherever you live, that’ll act as your realtor from this list.
- How Will I Agree On The Level Of Repair Job Needed?
Determining how much your home needs for repairs can be a major area of disagreement before a spouse finally agrees to sell a house. One spouse might think that the house needs more work done before it’s market-ready. For this reason, it’s important to include in your separation agreements which repairs you’re going to prioritize. If you still can’t agree on these, then it might be a good idea to go with your realtor’s recommendations for repairs.
- Who Will Cover The Costs Of the Repairs?
If you’ve decided which repairs you’ll have done on the house, then the next step is to ask your lawyer to help you determine who will cover the cost of the repairs. If it’s going to be the both of you, then what percentage is each of you going to bring? If only one of you can cover the fees upfront, then you’ll need to work out a payment plan to reimburse them after you’ve shared the proceeds from the home sale.
- How Will You I Share Proceeds And Liabilities From The Sale Of My Home?
Under normal circumstances, spouses should be dividing proceeds from home equally, but, sometimes, there might be special circumstances that require a more customized share distribution.
If, for instance, one partner took care of the bulk of all expenses connected to the house since the separation, that is, the mortgage and the repairs, then that partner might need to be reimbursed first before sharing can commence. All of this will need to be reflected in writing before your house goes to sell.
Conclusion
It’s easy for seemingly minor details to slip past you as you plan to sell your house and split your assets during a divorce, causing unnecessary stress for you and your family. Using this article as a checklist for questions to make sure you ask your lawyer, you can make sure nothing will ambush you in the future that you didn’t prepare for, leaving everyone involved on the solid legal ground.
Law
Choosing the Right Will and Trusts Attorney for Your Estate Planning Needs


Understanding the Difference: Wills vs. Trusts
Decoding Wills: What You Need to Know
Wills are fundamental legal documents that dictate how an individual’s assets will be distributed upon their death. At their core, a will serves as a blueprint for an individual’s last wishes, ensuring that their belongings are passed on to the designated heirs or beneficiaries. It typically outlines who will inherit specific assets, who will manage the estate (the executor), and other stipulations such as guardianship provisions for minor children. A will only goes into effect after probate, a legal process that validates the will and oversees the distribution of assets under court supervision.
Importantly, the drafting of a will requires careful consideration of various factors including the specific language to be used, adherence to state laws, and the individual’s personal wishes and circumstances. Many people overlook the nuances of state probate laws, which can significantly impact how a will is executed and the timeline for asset distribution. This is why consulting with a will and trusts attorney is often essential, as they can provide guidance on minimizing legal complications and ensuring compliance with state requirements. Furthermore, a will is public record once it enters probate, which means the details of an estate can be accessed by anyone, raising concerns for individuals who may prioritize privacy over transparency.
Trusts Unveiled: More than Just a Safety Net
Trusts are often regarded as more versatile and dynamic than wills, offering a range of options for estate planning that can be tailored to meet specific financial and personal needs. A trust is a legal arrangement where a third party, known as a trustee, holds assets on behalf of beneficiaries. Trusts can be structured to take effect during and after the grantor’s lifetime, providing a means to manage estate assets in a way that a simple will cannot. One of the most significant advantages of a trust is that it allows for the direct transfer of assets to beneficiaries, bypassing the lengthy and often costly probate process, effectively keeping the estate private.
Different kinds of trusts serve distinct purposes; revocable living trusts can be altered or revoked during the grantor’s life, providing flexibility, while irrevocable trusts generally cannot be changed once established, but they offer powerful estate tax benefits. Additionally, certain trusts can mitigate tax liabilities, offer protection against creditors, or ensure that assets are managed responsibly for beneficiaries who may be minors or those who struggle with financial management. The breadth of options available within the realm of trusts is vast, allowing individuals to devise complex estate plans that can respond to changing life circumstances, financial markets, and personal goals more adeptly than a traditional will.
Choosing Between a Will and a Trust: Factors to Consider
The decision between creating a will and a trust involves multiple factors that individuals must assess based on their unique financial situations, family dynamics, and long-term goals. One of the first considerations is the size and complexity of the estate; larger estates with varied types of assets might warrant the creation of a trust to avoid probate and facilitate smoother asset distribution. Conversely, for those with smaller or more straightforward estates, a will may suffice.
Another essential factor is the level of control desired over asset distribution. Trusts can provide specific instructions on when and how beneficiaries receive their inheritance, which can be vital in cases where individuals wish to protect minors or provide for someone with special needs. If maintaining privacy is a paramount concern, trusts excel as they bypass the public nature of probate proceedings associated with wills. Additionally, tax implications and strategies for minimizing taxes on inheritance can make trusts more attractive for certain individuals.
Ultimately, the determination between a will and a trust is heavily influenced by personal circumstances, with many individuals opting for a combination of both to maximize the benefits and protections afforded by each legal instrument. Engaging with a seasoned estate planning attorney can significantly aid in navigating these considerations and developing a tailored approach that aligns with one’s specific estate planning objectives.
Key Qualities to Look for in Your Estate Planning Attorney
The Role of Experience: Why It Matters
When searching for an estate planning attorney, one of the foremost qualities to consider is experience. An attorney’s years of practice and their familiarity with estate planning nuances can significantly impact the quality and effectiveness of the estate plan created. They should possess a strong understanding of state-specific laws, tax implications, and the intricacies of both wills and trusts which vary considerably across jurisdictions. Experienced attorneys bring insights gleaned from past cases and can foresee potential pitfalls, ensuring that the estate plan stands robustly against challenges that may arise during its execution.
A deeper level of experience involves exposure to a diverse range of estate planning scenarios, from simple wills for individuals with modest estates to complex trust arrangements involving business interests, real estate holdings, and blended family dynamics. The attorney’s past cases can offer tangible evidence of their problem-solving capabilities and their approach to finalizing estate plans that ensure client wishes are honored while minimizing risks. Moreover, an attorney’s track record in handling probate or estate litigation can be invaluable should disputes arise after the passing of the individual, thereby underscoring the importance of selecting a knowledgeable and well-rounded practitioner in the field of estate law.
Communication Skills: Finding Your Ideal Advocate
Effective communication is critical in the relationship between you and your estate planning attorney. You should seek an attorney who can articulate complex legal concepts in a clear and understandable manner, allowing you to fully comprehend your options and make informed decisions. A good attorney will take the time to listen to your specific needs, concerns, and goals, ensuring that the estate plan reflects your unique wishes. They should provide reassurance as you navigate the sensitivities associated with estate planning decisions, often involving family dynamics and future uncertainties.
Additionally, inquire about their subsequent communication style and responsiveness to emails or phone calls, as a high level of accessibility can greatly enhance the overall experience. Establishing a rapport with your attorney can also foster an environment of trust, which is essential when discussing personal and often emotionally-charged topics such as inheritance, guardianship, and family legacies. Remember, the estate planning process is not about just completing a set of legal documents; it is about building a long-term relationship with a legal partner who will advocate for your best interests across any future circumstances.
Trustworthiness: Building a Solid Foundation
Trustworthiness is arguably one of the most vital qualities to seek in your estate planning attorney. Given the sensitive nature of estate planning, which often includes discussions regarding finances, personal relationships, and future intentions, finding a trustworthy attorney will allow you to feel secure in sharing such sensitive information. A trusted attorney should display integrity, transparency, and a genuine commitment to helping you achieve your goals.
Research their reputation within the community, beginning with reviews and testimonials from former clients, as well as recommendations from other professionals, such as financial advisors or tax consultants. Additionally, consider their standing within professional organizations or bar associations, as active involvement in the legal community can signal a commitment to ongoing education and ethical practice. Ultimately, the security of knowing that your estate planning attorney has the best interests of your family at heart and is dedicated to ensuring that your legacy is honored can provide immense peace of mind.
Questions to Ask During Your Initial Consultation
Unveiling Their Approach: Strategies for Your Estate
During your initial consultation with a potential estate planning attorney, it is essential to inquire about their approach to estate planning. Understanding their overarching strategies allows you to gauge if their philosophy aligns with your needs. Engage them on questions about how they tailor estate planning services to reflect individual client circumstances, the importance of flexibility within estate plans, and how proactive they are in anticipating changes to laws that may affect your estate.
It can also be beneficial to discuss their approach toward educating clients throughout the process. A quality attorney will ensure you understand every step of the estate planning journey, providing explanations of how each part of the plan fits into your overall wishes. Additionally, assess their methods for maintaining an ongoing relationship with their clients, as planning for the future is not a one-time task. Inquire about how they will modify your estate plan to adapt to changes in personal circumstances or new legal developments, ensuring that your plan continues to serve your family’s best interests effectively.
Understanding Fees: What’s Fair and What Isn’t
The cost of hiring an estate planning attorney is often a pivotal consideration. Different attorneys charge different fee structures; therefore, it is vital to discuss fees upfront during the initial consultation to avoid misunderstandings down the line. Common billing methods include hourly rates, flat fees for specific services, or retainers that cover various aspects of estate planning. Asking for a detailed breakdown of potential costs associated with the creation of wills, trusts, and other estate planning options can provide transparency into what you should expect.
In addition, understanding how long the process may take and any anticipated ongoing expenses related to asset management or modifications can alleviate future surprises. A fair attorney will be upfront about their fees, the value they provide, and will willingly share references for potential expenses based on various scenarios. Ultimately, the goal is to invest wisely in an attorney who provides both expertise and genuine service without subjecting you to unanticipated costs or complications.
Assessing Compatibility: Finding Your Perfect Match
Compatibility with your estate planning attorney is paramount; a positive rapport fosters collaboration and openness, which are critical in addressing sensitive estate matters. You should feel comfortable discussing intricate family dynamics or personal preferences without fear of judgment. Take the time to evaluate how well the attorney listens to your concerns, respects your values, and aligns with your vision of how your legacy should be managed.
Observing how they respond to your questions and how receptive they are to your insights can also offer a glimpse into their working style. An attorney who is genuinely interested in your perspective will be better equipped to create a comprehensive and thoughtful estate plan that resonates with your desires. Additionally, consider the attorney’s communication style—do they follow up with you in a timely manner, and do they make you feel valued as a client? Ensuring that all these elements align will contribute heavily to the effectiveness of your estate planning experience.
Navigating the Complexities of Estate Planning
Tax Implications: Avoiding Costly Mistakes
One of the trickiest aspects of estate planning is navigating the myriad tax implications that accompany asset transfer upon death. There are different tax responsibilities for estates, heirs, and trusts that can significantly impact the distribution and value of the assets left behind. Estate taxes, which can impact larger estates, require careful planning to minimize potential liabilities. Proper structuring through the use of trusts, gifts, or family limited partnerships can help mitigate exposure to these taxes.
Moreover, understanding the taxable assets within an estate, including real estate and investments, is essential. The key is to work with an attorney who can position your estate to take advantage of potential exclusions, deductions, and credits that can reduce the overall tax burden borne by heirs. Furthermore, be aware of state-level estate and inheritance taxes that can vary and can catch individuals by surprise if not accounted for properly. Proactive tax planning ensures that the wealth you intend to pass on to your heirs is preserved as much as possible, ultimately safeguarding their inheritance against unnecessary tax liabilities.
Updating Your Estate Plan: When and Why It’s Crucial
Estates are not static; they evolve as individuals and families encounter major life changes. Regularly reviewing and updating your estate plan is crucial to ensure that it remains aligned with your current circumstances and priorities. Key life events such as marriage, divorce, births, deaths, or significant financial changes should prompt a thorough reassessment of your estate documents. Additionally, major shifts in law or tax policy can also necessitate updates to an estate plan to safeguard against new liabilities or compliance issues.
Many individuals overlook the necessity of change until faced with the reality of probate or asset distribution challenges. Updated plans ensure the continuity of your intentions across a lifetime, allowing for proper asset management, alteration of beneficiaries, and amendments regarding guardianship for minors. Engaging with your estate planning attorney on a regular basis, or at least every few years, not only keeps your documents up to date but fosters ongoing dialogue that may uncover new strategies or considerations to enhance your estate plan further.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid: Lessons from Real Cases
As you embark on the estate planning journey, it is imperative to learn from the common pitfalls that have troubled others. One of the most frequent mistakes is failing to communicate your estate plan to your family members. Lack of transparency can lead to confusion, disputes, and in worst-case scenarios, prolonged litigation after your passing. Open discussions can promote understanding and prevent misunderstandings among family members regarding asset allocation and intentions.
Another common pitfall is neglecting to update beneficiary designations on assets such as life insurance policies, retirement accounts, or bank accounts after key life events. Designations generally supersede instructions left in wills or trusts; therefore, failing to keep them current creates potential for unintended distributions that may not align with your wishes.
Moreover, many individuals underestimate the complexity of estate taxes and the significant impacts they can have on the estate value and the inheritances left to heirs. Lack of comprehensive tax planning or strategic asset division can lead to unnecessary financial burdens on the beneficiaries. To avoid these pitfalls, consider seeking professional guidance from an estate planning attorney who can provide specific strategies on how to navigate the most common challenges faced and create a lasting plan that serves your family’s best interests long after you are gone.
Law
Legal Cash Advances: Bridging the Financial Gap Between Health Needs and Justice


When an accident lands you in both the emergency room and a courtroom, the medical bills can pile up long before a settlement check ever arrives. That delay isn’t just a numbers game—it has real-world consequences for your well-being. Mounting research links financial strain to higher risks of anxiety, chronic disease flare-ups, and delays in necessary care. In other words, the money you need to stay healthy often arrives after health has already taken a hit. That’s where legal cash advances step in, offering plaintiffs a lifeline that keeps medical and everyday expenses on track while a lawsuit runs its course.
What Exactly Is a Legal Cash Advance?
A legal cash advance—sometimes called pre-settlement funding—is a non-recourse advance offered to plaintiffs with a pending personal injury or similar claim. Because repayment is contingent on winning or settling the case, it differs from a traditional loan: if the case is unsuccessful, the advance typically does not have to be repaid. The American Bar Association notes that consumer-focused litigation funding is usually capped at relatively modest amounts and is designed to cover day-to-day living or treatment costs rather than bankroll an entire trial strategy.
Why Financial Stress Is a Health Issue
It’s easy to treat money and medicine as separate concerns, yet public health data tells another story. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that 90 percent of the nation’s $4.5 trillion annual health-care spend relates to chronic and mental health conditions—conditions that are aggravated by stress. Stress hormones such as cortisol can disrupt sleep, raise blood pressure, and weaken the immune response, creating a vicious cycle in which unresolved medical bills exacerbate illness, and worsening illness amplifies costs.
The Real-World Cost of Waiting for a Settlement
Even a short gap between injury and compensation can destabilize a household budget. According to the CDC’s National Health Interview Survey, nearly one in ten U.S. adults lives in a family that has struggled to pay medical bills during the previous 12 months, with higher percentages among those already managing disabilities. For plaintiffs, the situation is often more acute: regular income may dip due to lost work hours, while co-pays, physical therapy, and prescription expenses spike.
How a Cash Advance Supports Ongoing Care
Here’s where a legal cash advance becomes more than a financial tool—it can be a health-preserving measure:
- Continuity of treatment– Plaintiffs can afford recommended follow-up visits, diagnostic imaging, or prescription refills instead of postponing care until “after the settlement.”
- Reduced cost-related non-adherence– Studies show that people under financial pressure are more likely to skip doses or self-ration medication. Access to immediate funds helps prevent that risky behavior.
- Mental-health relief– Knowing that rent and utility payments are covered lightens the cognitive load, letting you focus on physical recovery and the legal process, not late fees.
A Deeper Look at Plaintiff Advantages
For readers who want to unpack how plaintiffs specifically benefit, beyond the medical angle, take a look at an in-depth exploration of the key plaintiff advantages offered by legal cash advances. You’ll find a detailed breakdown of fee structures, approval timelines, and risk considerations that complement the health-centered discussion here.
Due Diligence: Choosing a Reputable Funder
Not every funding offer is equal, and the wrong terms can undercut the very relief you’re seeking. Consider these checkpoints:
- Transparent pricing– Look for a clear, flat fee or interest schedule, laid out in plain English.
- Independent legal counsel– Ethical funders encourage your attorney to review the contract.
- No control over litigation strategy– As emphasized by ABA guidance, funding companies should not direct your attorney’s decisions.
Ask questions, read the fine print, and be wary of pressure tactics. A short-term fix that balloons into an oversized payoff can negate health and financial gains.
Potential Trade-Offs and How to Manage Them
Every financial tool carries downsides. Fees can be higher than conventional credit, and stacking multiple advances magnifies repayment obligations. Talk openly with your lawyer about realistic settlement ranges, how much of that amount a funder has first claim to, and what your net recovery might look like before signing anything. If the numbers no longer cover medical follow-up or household recovery, a smaller advance—or none at all—may be the healthier choice.
The Bigger Picture: Health, Justice, and Financial Stability
Legal cash advances aren’t a magic wand, but they do narrow the dangerous gap between injury-related expenses and eventual compensation. By easing cash-flow crunches, they help plaintiffs avoid treatment delays, medication lapses, and the stress spirals that chip away at recovery. That synergy between financial stability and health outcomes is why pre-settlement funding has become a recurring topic in both legal and public health circles.
When weighing your own options, ground the decision in credible data, a candid budget review, and professional legal advice. Do that, and a well-structured advance can serve as one more tool, alongside physical therapy sessions and follow-up lab work, on the road to reclaiming both health and financial peace of mind.
Read More: Jessica Ditzel
Law
A Detailed Overview of the Litigation Process


Litigation is the formal legal process used to resolve disputes between individuals, businesses, or other entities. This process plays a crucial role in ensuring justice in cases such as personal injury claims, contract disputes, and divorce proceedings.
If you are interested in Litigation Crowdfunding, check this read Litigation Crowdfunding: Do’s and Don’ts — 8 Tips to Maximize Success
Civil Litigation and Court Jurisdiction
Civil litigation can occur in either state or federal courts, depending on the nature of the dispute. In the United States, the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure govern cases in federal courts, aiming to provide a just, speedy, and cost-effective resolution for all involved parties.
The Litigation Process
While the specifics of litigation can vary by jurisdiction, the general process follows these key steps:
1. Filing a Complaint
When the plaintiff formally submits a claim to the court, describing the disagreement and the legal foundation for their position, the procedure officially starts. After that, the court notifies the defendant about the lawsuit through papers.
2. Pre-Trial Motions and Discovery
Motions may be submitted by any party asking the judge to render particular decisions. Typical motions consist of: A motion to compel discovery asks the court to mandate that the other party provide crucial information; A motion for summary judgment is a proposal to settle a case without a full trial when one side is legally entitled to win and the facts are undeniable.
The next step is the discovery phase, during which both parties collect evidence, share documents, and conduct depositions in order to strengthen their views.
3. Trial Proceedings
The case goes to trial if it is not dismissed or settled. Both sides offer arguments and supporting documentation during the trial.
Witnesses may be cross-examined and called to testify.
The burden of proving claims, such as proving negligence in a personal injury case, usually rests with the plaintiff.
4. Verdict and Judgment
The verdict of the case is decided by a jury or a judge. The right to a jury trial is guaranteed by the U.S. Constitution if the plaintiff seeks monetary damages over $20, unless all parties agree to forgo this right. A judge typically renders a decision in cases involving non-monetary remedy, like an injunction.
5. Appeals and Enforcement
A party may file an appeal with a higher court to request a reconsideration of the decision if they are unhappy with it. The verdict is implemented through the judicial system if the appeal is denied.
Arbitration: An Alternative to Litigation
Arbitration is a form of alternative conflict resolution that is useful for people who want to avoid drawn-out and expensive court cases. An unbiased arbiter considers the matter and renders a binding ruling in lieu of a trial, which frequently results in a quicker and more economical resolution.
The Problem of Frivolous Litigation
Although frivolous lawsuits—cases brought with little legal basis, frequently as part of class actions or mass tort claims aiming at financial gain—have become a burden on the litigation system, which is meant to settle legitimate issues. These cases can cost defendants a lot of money, take years to conclude, and deplete the court’s resources. Resolving this issue is essential to preserving a just and effective judicial system.
One essential method for settling conflicts and defending legal rights is still litigation. Businesses and people can successfully manage legal disputes by being aware of the procedure, available options such as arbitration, and the difficulties presented by pointless litigation. Being well-informed is essential to getting the best result whether filing a lawsuit or defending against one.
Resource:https://instituteforlegalreform.com/blog/what-is-litigation/
Read More: jacqulyn elizabeth hanley
-



 Biography7 years ago
Biography7 years agoJacqulyn Elizabeth Hanley is the Mother of Liza Soberano?
-



 Biography7 years ago
Biography7 years agoAmanda Levy Mckeehan Biography, Family, Net Worth, Age, Affairs, Facts
-



 Home6 years ago
Home6 years agoEpson L3110 Driver Free Download Latest Updated Version
-



 Games5 years ago
Games5 years agoBest Free To Play MMORPG To Try This 2021
-



 Biography7 years ago
Biography7 years agoWho is Rose Dorothy Dauriac? Scarlett Johansson Daughter?
-



 Home7 years ago
Home7 years agoLiza Soberano Biography, Age, Family and Boyfriends
-



 Biography7 years ago
Biography7 years agoJessica Ditzel Secret Information that Nobody Knows | Joe Rogan’s Wife
-



 Biography7 years ago
Biography7 years agoWhat is the relation of Nathaniel Larry Osorno with Liza Soberano?